

From Farm to Fortune: The Municipality’s Crop Boom, Livestock Boom, and Growth-Driven Policies

Date Created : 11/14/2025 6:41:30 AM : Story Author : Ghanadistrictscom
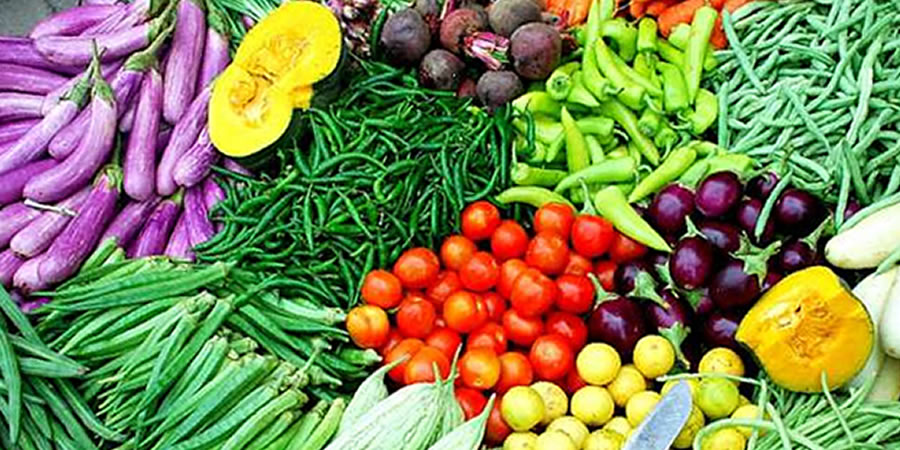
Crops: maize, cassava, vegetables, and more
Among the major crops produced in the municipality, maize and cassava constitute foundational staples for local diets and market supply. Vegetables—particularly pepper, okra, and cabbage—have emerged as high-value crops with strong demand in urban centers and peri-urban markets. Cabbage, in particular, has shown notable growth potential as farmers leverage the municipality’s environmental assets, including water bodies and irrigation opportunities.
A recurring observation across agricultural reporting is the expansion of production volumes despite formidable headwinds. This trend is visible in Table 1.8, which provides a snapshot of average production levels for the municipality’s principal crops. The data indicate gradual but steady growth, reflecting improvements in farm management, adoption of improved seed varieties, and access to input support. While specific figures are not reproduced here, the qualitative takeaway emphasizes a positive trajectory in crop output across the board.
Irrigation and water resources underpinning horticulture
A salient development in cabbage cultivation—and in horticulture more broadly—has been the strategic use of water resources. The Nsakyi River, with its riparian zones and surrounding water bodies, serves as a critical irrigation source, enabling farmers to operate beyond the constraints of rainfall patterns. Farmers along the riverbanks have adopted irrigation practices that stabilize yields and extend the cropping season. In some instances, research facilities and government staff also contribute to irrigation management on nearby research lands, reinforcing knowledge transfer and experimentation in best practices. The average observed farm size is approximately 0.5 acre, reflecting a predominance of smallholder operations that collectively contribute substantially to local food supply and income.
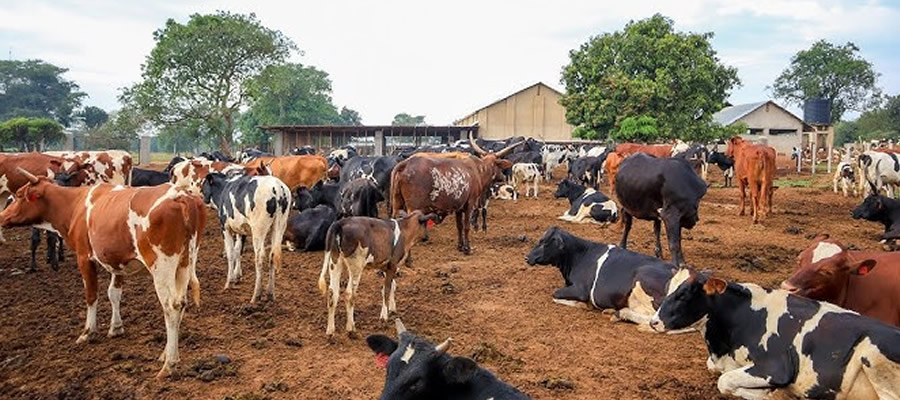
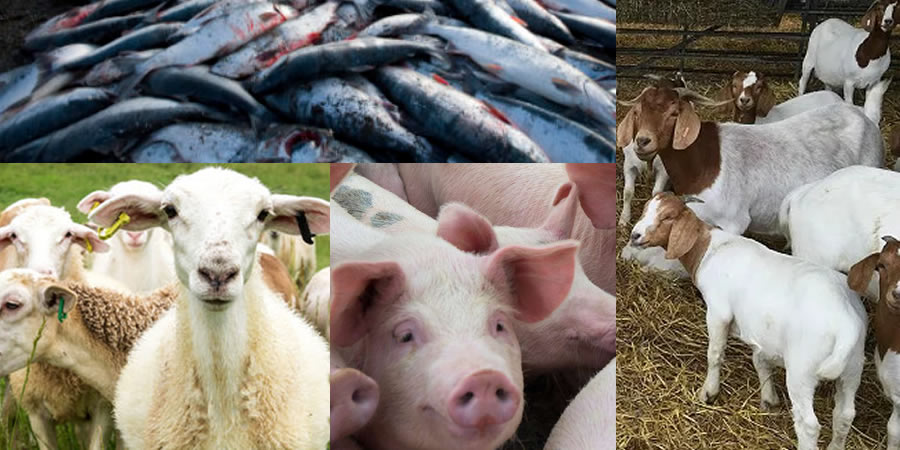
Animal husbandry: macro and micro livestock, poultry
The municipality supports a diversified livestock sector, spanning macro and micro categories. Macro livestock includes sheep, goats, pigs, and cattle, while micro livestock encompasses smaller stock such as grass cutters and rabbits. Poultry products add another vital dimension to the agricultural mix, with effects on household nutrition as well as market sales. The integration of crop and livestock farming—especially in mixed-farming systems—helps optimize farm resources, manage waste, and improve overall farm resilience.
Policy-driven programs and extension support
To bolster productivity and modernize farming practices, several programmes have been promoted by the Municipal Agricultural Directorate. Key initiatives include:
- Backyard Farming promotion: Encouraging households to diversify food production at scale, improve nutrition, and generate supplementary income.
- Planting for Food and Jobs (PFJ): A national program designed to boost domestic food production, reduce reliance on imports, and create employment opportunities across the agricultural value chain.
- Rearing for Food and Jobs: A livestock-focused initiative aimed at expanding animal protein production and supporting pastoral livelihoods.
- Deployment of additional Agricultural Extension Officers: Strengthening advisory services to farmers, improving dissemination of best practices, pest and disease management, soil fertility improvement, and post-harvest handling.
Outlook: growth amid constraints
The municipality’s agricultural sector appears poised for continued growth, driven by smallholder dynamism, irrigation-enabled horticulture, and an expanding livestock market. Public investment in extension services and incentivized farming programs reinforces the support framework for farmers adapting to land-use pressures. However, lasting progress will require attention to land-use planning, sustainable land management practices, and ongoing access to affordable inputs, credit, and markets.
Implications for stakeholders
- Farmers: Embrace diversified cropping and livestock systems, invest in water-efficient irrigation, and participate in extension services to adopt improved varieties and sustainable practices.
- Local government: Align land use planning with agricultural priorities to reduce land erosion and fragmentation, while scaling up support for water resource management and climate-resilient farming.
- Private sector and development partners: Explore opportunities in value addition, agro-processing, storage facilities, and logistics to strengthen market access for crops and livestock products.
- Researchers and educators: Continue collaborative work with the Ministry of Agriculture and CSIR-affiliated facilities to refine agronomic practices, pest management, and post-harvest technologies.









 facebook
facebook
 twitter
twitter
 Youtube
Youtube
 +233 593 831 280
+233 593 831 280 0800 430 430
0800 430 430 GPS: GE-231-4383
GPS: GE-231-4383 info@ghanadistricts.com
info@ghanadistricts.com Box GP1044, Accra, Ghana
Box GP1044, Accra, Ghana